
Master the Volume of a Pyramid: Easy Formula & Real Examples 2026
Introduction
Ever looked at the pyramids of Egypt and wondered how much space is actually inside those massive structures? You’re not alone. Understanding the volume of a pyramid isn’t just about ancient architecture. It’s a fundamental concept that pops up everywhere from geometry class to engineering projects.
The volume of a pyramid tells you how much three-dimensional space it occupies. Whether you’re working on a school assignment, designing a structure, or just curious about how mathematicians figure these things out, you’ve come to the right place. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about pyramid volume in plain English.
I’ll walk you through the formula, show you how to use it with real examples, and answer the questions that trip most people up. By the end, you’ll be calculating pyramid volumes like a pro.
What Exactly Is a Pyramid?
Before we dive into calculations, let’s get crystal clear on what we’re talking about. A pyramid is a three-dimensional shape with a polygon base and triangular faces that meet at a single point called the apex or vertex.
Think of it like a tent. The bottom can be any shape—square, triangle, rectangle, or even more complex polygons. The sides slope upward and come together at the top. The Egyptian pyramids have square bases, which makes them square pyramids.
The key parts you need to know are the base, the height, and the apex. The base is the bottom surface. The height is the perpendicular distance from the base to the apex. That perpendicular part matters because you measure straight up, not along the slanted edge.
The Simple Formula for Volume of a Pyramid
Here’s the formula you’ve been waiting for:
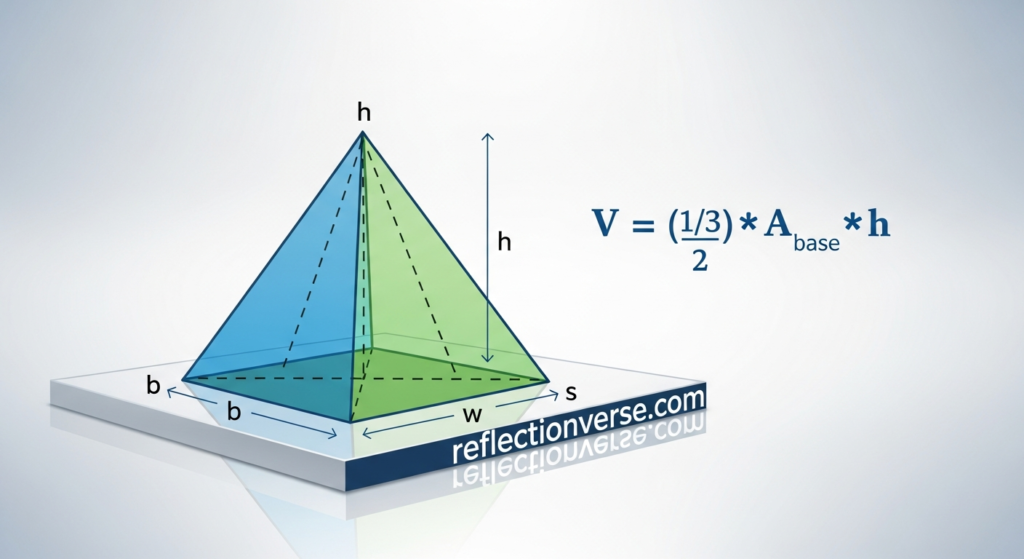
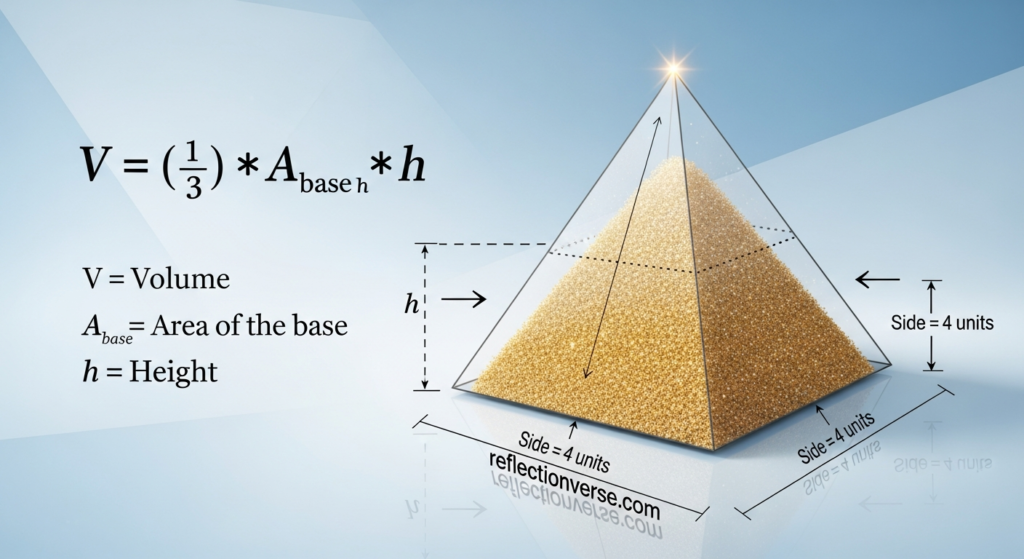
Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height
That’s it. Really. The volume of a pyramid equals one third of the base area multiplied by the height. This formula works for any pyramid, regardless of what shape the base is.
Why one third? Imagine filling a cube with smaller pyramids that have the same base and height. You’d need exactly three pyramids to fill that cube. That’s where the fraction comes from. It’s a mathematical relationship that’s been proven and tested for centuries.
The beauty of this formula is its simplicity. Once you know the area of the base and the height, you’re basically done. Just multiply them together and divide by three.
How to Find the Base Area
The base area depends entirely on what shape your base is. Let me break down the most common ones you’ll encounter.
Square Base If your pyramid has a square base, the area is simply side times side. A square with sides of 5 meters has an area of 25 square meters. Easy.
Rectangular Base For rectangles, multiply length times width. A base that’s 6 meters long and 4 meters wide gives you 24 square meters.
Triangular Base Triangle area is one half times base times height. If the triangle at the bottom of your pyramid has a base of 8 meters and a height of 6 meters, the area is 24 square meters.
Other Polygons For hexagons, octagons, or irregular shapes, you’ll need the specific formula for that polygon. Sometimes breaking the shape into smaller triangles or rectangles helps.
Step-by-Step: Calculating Volume with Examples
Let me show you exactly how this works with real numbers. We’ll start simple and build up.
Example 1: Square Pyramid
Imagine a pyramid with a square base where each side measures 10 meters. The height from the base to the apex is 15 meters.
First, find the base area. Since it’s a square, that’s 10 × 10 = 100 square meters.
Now apply the formula. Volume = (1/3) × 100 × 15.
That gives you (1/3) × 1,500 = 500 cubic meters.
See? Not so scary once you break it down.
Example 2: Rectangular Pyramid
Your pyramid has a rectangular base measuring 8 meters by 6 meters. The height is 12 meters.
Base area equals 8 × 6 = 48 square meters.
Volume = (1/3) × 48 × 12 = (1/3) × 576 = 192 cubic meters.
Example 3: Triangular Pyramid (Tetrahedron)
The base is a triangle with a base of 10 meters and a height of 8 meters. The pyramid’s height is 9 meters.
First, the triangle area is (1/2) × 10 × 8 = 40 square meters.
Volume = (1/3) × 40 × 9 = (1/3) × 360 = 120 cubic meters.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Everyone makes mistakes when learning this concept. Here are the big ones I see all the time.
Confusing Slant Height with Actual Height
The slant height is the distance along the face of the pyramid from the base to the apex. That’s not what you need. You need the perpendicular height, which goes straight up from the center of the base to the top. Always double check which measurement you’re using.
Forgetting to Divide by Three
Some people calculate base area times height and stop there. Remember, you must multiply by one third or divide by three. Without this step, your answer will be three times too large.
Using the Wrong Base Area Formula
If you have a triangle but use the square formula, your entire calculation falls apart. Make absolutely sure you know what shape your base is before you start calculating its area.
Mixing Up Units
If your base measurements are in meters but your height is in centimeters, convert everything to the same unit first. Otherwise, your volume will be meaningless.
Why This Formula Matters in Real Life
You might think pyramid volume is just abstract math, but it shows up in surprisingly practical places.
Architects and engineers use it when designing buildings with pyramidal roofs or structures. They need to know volume for material estimates and weight calculations. Landscape designers use it when planning pyramid-shaped garden features or monuments.
In manufacturing, pyramid-shaped containers and packaging require volume calculations for filling and shipping. Even in fields like geology, understanding the volume of pyramid-shaped rock formations helps with research and conservation.
The ancient Egyptians clearly understood these principles when building their pyramids. The Great Pyramid of Giza has a volume of roughly 2.5 million cubic meters. That’s an incredible amount of stone, and they calculated it thousands of years ago.
Different Types of Pyramids
While the basic formula stays the same, pyramids come in different varieties worth knowing about.
Regular Pyramid
This has a regular polygon as its base and the apex directly above the center. These are the most symmetrical and easiest to work with.
Right Pyramid
The apex sits directly over the centroid of the base. The height line makes a right angle with the base. Most textbook examples use right pyramids.
Oblique Pyramid
The apex doesn’t sit directly over the center of the base. The pyramid leans to one side. The volume formula still works, but finding the height becomes trickier.
Square, Triangular, Pentagonal, Hexagonal
These names describe the base shape. A square pyramid has four triangular faces, a triangular pyramid has three, and so on.
Advanced Applications and Variations
Once you master the basic formula, you can tackle more complex scenarios.
Finding Height When You Know Volume
Sometimes you know the volume and base area but need to find the height. Rearrange the formula: Height = (3 × Volume) / Base Area.
If a pyramid has a volume of 600 cubic meters and a base area of 150 square meters, the height is (3 × 600) / 150 = 12 meters.
Truncated Pyramids (Frustums)
A frustum is a pyramid with the top cut off parallel to the base. The volume formula gets more complicated. You need both the top and bottom base areas and the height between them.
The formula becomes: Volume = (h/3) × (A1 + A2 + √(A1 × A2)), where h is the height, A1 is the bottom base area, and A2 is the top base area.
Comparing Pyramid and Prism Volumes
A prism with the same base and height as a pyramid has exactly three times the volume. This relationship helps you check your work. If you calculate a pyramid volume and it seems too large, you might have forgotten to divide by three.
Tips for Success with Volume Calculations
Here’s what works when you’re solving these problems.
Always sketch the pyramid first. Draw the base separately and label all measurements. Visual aids prevent confusion about which numbers go where.
Write out the formula before plugging in numbers. This keeps your work organized and helps you spot errors.
Double check your base area calculation before moving to the final volume. Most mistakes happen at this stage, not in the final multiplication.
Keep your units consistent throughout. If you start with meters, finish with cubic meters. Label your final answer clearly.
Use a calculator for the arithmetic, especially when dealing with fractions and decimals. Mental math is great, but accuracy matters more.
Practice Makes Perfect
The only way to get comfortable with the volume of a pyramid is to practice with different examples. Try creating your own problems with different base shapes and measurements.
Start with whole numbers to build confidence. Then move to decimals and fractions. Challenge yourself with real-world scenarios like calculating the volume of a pyramid-shaped tent or a decorative structure.
Work backward sometimes. Give yourself a target volume and base area, then calculate what the height must be. This reinforces your understanding of how the variables relate to each other.
Check online resources for practice problems with answer keys. Work through them, compare your answers, and learn from any mistakes.
Conclusion
Understanding the volume of a pyramid opens doors to solving all kinds of geometric problems. The formula is beautifully simple: one third of the base area multiplied by the height. Whether you’re calculating the volume of a square pyramid, a triangular pyramid, or any other type, the same principle applies.
Remember to identify your base shape correctly, calculate that area accurately, and don’t forget to multiply by one third. Avoid the common mistakes like using slant height instead of perpendicular height or mixing up your units.
With the examples and tips in this guide, you’re equipped to tackle pyramid volume problems confidently. The more you practice, the more natural it becomes. What pyramid volume will you calculate first?
FAQs
What is the formula for the volume of a pyramid?
The formula is Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height. You multiply the area of the base by the perpendicular height, then divide by three. This works for any pyramid regardless of base shape.
Why do we multiply by 1/3 when calculating pyramid volume?
Three identical pyramids with the same base and height can perfectly fill a rectangular prism of that base and height. Since the prism’s volume is base area times height, each pyramid must be one third of that volume.
How do you find the height of a pyramid if you know the volume?
Rearrange the formula to solve for height. The equation becomes Height = (3 × Volume) / Base Area. Multiply the volume by three, then divide by the base area.
What’s the difference between slant height and perpendicular height?
Slant height measures along the outside face of the pyramid from base edge to apex. Perpendicular height measures straight up from the base center to the apex at a right angle. Always use perpendicular height for volume calculations.
Can you use the same formula for pyramids with different base shapes?
Yes. The volume formula works for square, rectangular, triangular, hexagonal, or any polygon base. Just calculate the correct base area for your specific shape, then apply the standard formula.
What is a regular pyramid?
A regular pyramid has a regular polygon as its base and its apex positioned directly above the center of that base. All the triangular faces are congruent, making it symmetrical.
How do you calculate the volume of a triangular pyramid?
First, find the triangle base area using (1/2) × base × height. Then use the pyramid formula: Volume = (1/3) × triangle area × pyramid height. Make sure you use the pyramid’s perpendicular height, not the triangle’s height.
What units should the volume of a pyramid be in?
Volume is always measured in cubic units. If your measurements are in meters, the volume is in cubic meters. If measurements are in feet, volume is in cubic feet. The units must be consistent throughout your calculation.
What is the volume of the Great Pyramid of Giza?
The Great Pyramid has an estimated volume of approximately 2.5 million cubic meters. With a square base of about 230 meters per side and a height of roughly 147 meters originally, it demonstrates the pyramid volume formula on a massive scale.
Can you find pyramid volume without knowing the height?
Not directly with the standard formula. You need either the perpendicular height or enough information to calculate it. Sometimes you can use the Pythagorean theorem with slant height and base measurements to find the perpendicular height first.
Also read reflectionmverse.com


